Ever wondered how a massive video file, straight from a camera, gets shrunk down small enough to stream on your phone without eating up your entire data plan? That’s the magic of a video encoder.
Think of it as a highly efficient digital packer. It takes raw, bulky video data and skillfully compresses it into a compact, stream-friendly format perfect for platforms like YouTube, Netflix, or Twitch. This process isn’t just helpful; it’s the very foundation of modern online video.
What Is a Video Encoder in Simple Terms

Let’s try an analogy. Imagine trying to send a giant, life-sized portrait through the mail. It’s just too big for a standard envelope. A video encoder tackles this same issue for video files. It takes enormous, uncompressed video—which can easily be several gigabytes for just a few minutes of footage—and cleverly shrinks it down into a much more manageable size.
This compression is what makes virtually all online video possible. Without it, streaming a 4K movie would demand a ridiculously fast internet connection, and buffering would be a constant frustration. The encoder’s job is to find that perfect balance: shrink the file size dramatically while keeping the video looking crisp and clear.
The Three Core Jobs of an Encoder
At its core, a video encoder has three critical responsibilities that get a video ready for its journey across the internet. Each step is essential for delivering a smooth, high-quality viewing experience, no matter what device or network someone is using.
An encoder’s main challenge is balancing three competing factors: file size, video quality, and processing speed. A great encoding process finds the sweet spot where video looks sharp, file size is small, and there’s no lag.
To make this clearer, let’s break down these three primary jobs. The table below gives a quick overview of what an encoder does and why each function is so important for streaming.
Core Functions of a Video Encoder at a Glance
| Function | Description | Why It Matters for Streaming |
|---|---|---|
| Compressing | Intelligently removes redundant or less noticeable data to drastically reduce the overall file size. | Smaller files require less bandwidth, which prevents buffering and allows for smooth playback even on slower connections. |
| Converting | Changes the video file into a standardized format (like MP4) that is compatible with various devices and platforms. | Ensures your video can be played back on computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and web browsers without compatibility issues. |
| Packaging | Organizes the compressed video and audio data into a bitstream, making it ready for transmission over the internet. | This final step prepares the data to be sent efficiently from the server to the viewer’s screen in real-time. |
In short, these three functions work in harmony to transform raw footage into a polished, streamable asset that anyone can watch, anywhere.
How the Video Encoding Process Actually Works
So, what does a video encoder really do? Let’s trace a video file’s journey from its bulky, raw state into a sleek, streamable format. The whole process is a clever mix of analysis, prediction, and strategic data removal, all aimed at shrinking the video without destroying its quality.
The secret sauce is a technique called inter-frame compression. Instead of treating every single frame of a video as a completely new picture, the encoder gets smart and looks for what stays the same from one frame to the next.
Think about a classic cartoon. The animator doesn’t painstakingly redraw the entire background in every cell; they just draw the parts that move, like a character walking against a static scene. A video encoder works on the same principle.
It starts by identifying a full, complete picture, known as an I-frame (or keyframe). Then, for the next handful of frames, it only records the pixels that actually change. These in-between frames are called P-frames (predicted frames) and B-frames (bi-directional predicted frames). This approach is vastly more efficient than saving all the data for every frame.
Following the Encoder’s Rulebook
To pull off this compression magic, the encoder has to follow a strict set of rules called a codec (which is short for coder-decoder). You can think of the codec as the encoder’s instruction manual. It lays out the exact algorithms and methods for shrinking the video data, which ultimately determines the final balance between file size and visual quality.
The diagram below gives you a bird’s-eye view of this surprisingly simple workflow.
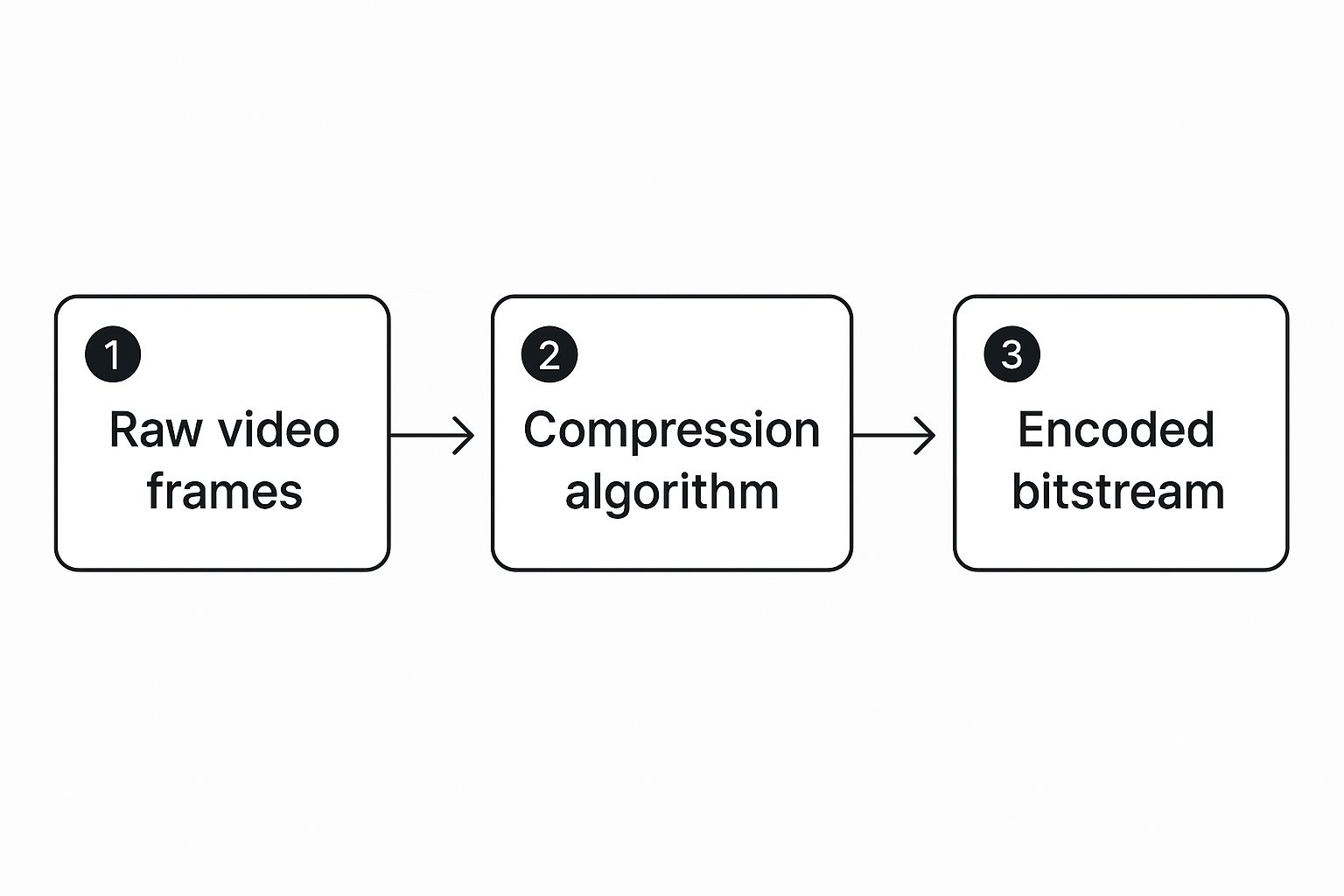
As you can see, raw video frames go in, the compression algorithm works its magic, and a tidy, encoded bitstream comes out the other side, ready to be sent across the internet. It’s this very process that took video from clunky physical tapes to the seamless streaming we take for granted today.
The global video encoder market was valued at USD 2.18 billion and is expected to reach nearly USD 2.92 billion by 2032. This growth shows just how critical high-quality, real-time streaming has become.
Understanding Video Codecs: The Encoder’s Language
If the video encoder is the engine, then the codec is the specific kind of fuel it’s designed to run on. A codec—a portmanteau of coder-decoder—is basically the rulebook or algorithm that an encoder uses to compress video data. Think of it as a specialized language for making video files smaller.
The choice of codec is a big deal. It directly impacts the final balance between video quality, file size, and compatibility. One codec might give you a stunningly clear picture in a tiny file, but it might only work on the latest devices. Another might be less efficient but will play on virtually any screen you can find.
H.264: The Universal Standard
For a long time, H.264 (AVC) has been the undisputed king of the video world. Its superpower? Unbeatable compatibility. You’ll find it supported by just about every web browser, smartphone, smart TV, and streaming service out there.
This universal reach makes H.264 a safe and incredibly reliable bet. If your goal is to get your video in front of the largest possible audience without worrying about playback errors, this is your go-to codec.
Choosing a codec is a strategic decision. You’re trading compatibility for efficiency. H.264 offers maximum reach, while newer codecs like H.265 prioritize quality at lower bitrates.
H.265: The Efficient Successor
Enter H.265 (HEVC), the modern, high-efficiency heir to the throne. Its main claim to fame is that it can deliver the same visual quality as H.264 while using about half the data. That’s a massive improvement.
This incredible efficiency is what makes streaming crisp 4K and 8K video possible without needing a monstrous internet connection. While it isn’t quite as universally supported as H.264 yet, H.265 is the new standard for ultra-high-definition content.
Want to dive deeper into the technical side of things? We break it all down in our guide on what video codecs are and the magic they perform. Getting a handle on codecs is the key to truly understanding what a video encoder is all about.
Hardware Encoders Versus Software Encoders
When it’s time to pick a video encoder, you’re at a fork in the road. Do you go with a dedicated machine built for the job, or a versatile program that runs on your computer? This is the core difference between hardware and software encoders, and each has its own distinct advantages.
Think of a hardware encoder as a specialized piece of equipment, like a professional pizza oven in a bustling restaurant. It’s a physical box designed to do one thing—encode video—and do it exceptionally well, without fail. It takes the heavy lifting off your computer’s main processor, so your system can focus on other things.
A software encoder, on the other hand, is an application you install on your computer. It uses your computer’s own processing power (the CPU) to get the job done. This is more like using a high-end convection setting on your home oven. It’s powerful and can produce great results, but it’s sharing resources with anything else you might be cooking up at the same time.
Choosing Your Encoding Engine
So, which one is right for you? It really comes down to what you’re trying to accomplish.
A professional broadcast studio with a 24/7 live channel will almost always bet on a hardware encoder. They need rock-solid stability and performance that won’t buckle under pressure. For them, reliability is everything.
But if you’re a gamer or a creator just starting out, a software encoder is often the more practical choice. It’s affordable (many are free!), flexible, and perfect for figuring out how to stream live video. You can easily update the software and tweak settings without shelling out for new gear.
The trade-off is pretty straightforward: Hardware gives you dedicated power and stability, while software offers flexibility and a lower barrier to entry. There’s no “better” option—just the right tool for your specific job.
Hardware Encoder vs Software Encoder A Quick Comparison
To make the choice a bit clearer, let’s put them head-to-head. This table breaks down the key differences to help you see which approach lines up with your streaming goals.
| Feature | Hardware Encoder | Software Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | High and consistent; dedicated processing means minimal system impact. | Variable; depends heavily on the computer’s CPU and other running tasks. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for the dedicated physical device. | Lower upfront cost, often free or included with streaming software. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; features are tied to the device’s firmware and are harder to update. | Highly flexible; can be updated easily with new features, codecs, and improvements. |
| Use Case | Professional broadcasting, live events, and mission-critical streaming. | Casual streaming, VOD content creation, and situations needing versatility. |
Ultimately, whether you need the dedicated workhorse of a hardware encoder or the adaptable nature of a software solution depends entirely on your production needs and budget.
So, we’ve covered the what and the how of video encoders. But why should you really care? The answer becomes obvious the moment you hit “play” on any video, anywhere.
The entire modern streaming world—from live NFL games on ESPN+ to the latest vlog on YouTube—is built on a bedrock of smart, efficient encoding. Without it, the digital video experience as we know it would simply collapse.
Think about the last time you watched a video. Was it a smooth, crisp picture? Or a pixelated, buffering nightmare? Efficient encoding is the invisible hero that makes the former possible, preventing the frustrations that would otherwise be the norm. Raw 4K video files are just too gigantic to push through a typical internet connection. Encoding is what slims them down for the journey.
The Magic of Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
One of the cleverest tricks in modern streaming is something called adaptive bitrate streaming (ABS). This is the secret sauce that keeps your video playing without a hitch, even when your Wi-Fi signal is less than perfect.
Here’s the simple version: instead of one video file, the encoder creates several different versions, each at a different quality and file size. Your video player is smart enough to detect your internet speed in real-time and automatically picks the best version you can handle.
If you’re on a blazing-fast connection, you’ll see a beautiful, high-definition stream. The second your connection dips, the player instantly switches to a lower-quality version to keep the video playing smoothly. This on-the-fly adjustment is what separates a great viewing experience from a frustrating one.
Paving the Way for 4K, 8K, and Beyond
As we all start watching video in ultra-high resolutions like 4K and even 8K, encoders are more important than ever. The sheer amount of data in these formats is staggering. Advanced encoding is the only thing that makes it feasible to stream them without grinding the entire internet to a halt.
This is a big deal, and it’s driving serious investment. The global video encoder market was recently valued at USD 2.34 billion and is expected to grow to USD 3.48 billion by 2030. That growth is all thanks to better compression and more powerful hardware making high-res streaming a reality for everyone. You can dig deeper into these market trends over on 360iResearch.com.
At the end of the day, a video encoder isn’t just another piece of tech. It’s the essential bridge between enormous video files and the flawless, instant-on experience viewers now demand.
How APIs Make Complex Video Encoding Easy

For most developers and businesses, getting bogged down in the nuts and bolts of video encoders is a huge roadblock. It’s a specialized field, and frankly, it’s a distraction. Instead of wrestling with codecs, formats, and server configurations, a video API lets you hand off the entire workflow.
Think of it like hiring a world-class video engineering team with the click of a button. Rather than building an entire encoding pipeline from the ground up, you just send a simple request to the API. It handles all the heavy lifting behind the scenes, which can slash your development time from months to days.
Putting the Encoding Workflow on Autopilot
A robust API, like LiveAPI, turns video processing from a massive technical headache into a simple, solved problem. It gives you a straightforward way to plug professional-grade video capabilities directly into your app without the eye-watering upfront cost of specialized hardware or a team of experts.
This frees your team to do what they do best: building an incredible product and a fantastic user experience, not getting stuck managing a complex video pipeline.
The process often goes beyond just a single encode, too. For a deeper dive, you can check out our guide that breaks down the difference between encoding and its close relative, transcoding, and explains what video transcoding is.
With a video API, you’re essentially renting a massive, global encoding infrastructure on demand. You get instant access to perfectly optimized hardware and software, ensuring your video always looks amazing and performs reliably, whether you have ten users or ten million.
At the end of the day, an API transforms a complex, resource-draining task into a predictable and manageable service. It makes high-quality video a feature anyone can add to their application, not a privilege reserved for tech giants.
Common Questions About Video Encoders
Once you start digging into video encoders, a few questions always seem to surface. Let’s walk through some of the most common ones to help piece everything together.
Encoder vs. Transcoder: What’s the Difference?
This is easily the biggest point of confusion, and for good reason—the terms sound alike. But they have very distinct jobs in the video pipeline.
- An encoder does the first big compression. It takes the massive, raw video file straight from a camera and shrinks it down into a streamable format.
- A transcoder works with a file that’s already been compressed. Its job is to convert that file into different formats or bitrates.
Think of it this way: when you stream a live event, a transcoder is the tool that creates all the different quality options (1080p, 720p, 480p) so viewers can watch smoothly, no matter their connection speed. The initial squeeze is encoding; creating all the other versions from that first file is transcoding.
Why Do I Need an Encoder to Stream?
Honestly, you can’t stream without one. Raw video files are gigantic. We’re talking gigabytes of data for just a few minutes of high-quality footage. Trying to push that much data over the internet in real-time would be a disaster for even the fastest networks.
An encoder’s main purpose is to make that file small enough to travel across the internet efficiently. Without that crucial compression, your viewers would be stuck staring at a buffering wheel, or the stream would just fail completely.
Every single live stream you’ve ever watched, from a major sporting event to a gamer on Twitch, relies on an encoder. It’s the absolute first step that makes the whole process possible.
How Do I Choose the Right Encoder Settings?
Getting your settings right is all about finding the sweet spot between video quality and bitrate (how much data you’re sending every second). A higher bitrate usually gives you a crisper picture, but it demands a faster and more reliable internet connection to pull it off.
First things first, run a speed test to see what your upload bandwidth looks like. A good rule of thumb is to set your streaming bitrate to no more than 75% of your sustained upload speed. This leaves a little headroom for network hiccups.
If you’re not sure where to begin, streaming platforms like YouTube and Twitch offer excellent guides with recommended settings for different resolutions and frame rates. They’re a fantastic starting point for finding the perfect balance for your setup.
Ready to take the complexity out of your video workflow? LiveAPI provides a powerful, developer-friendly solution to manage all your encoding and streaming needs, so you can focus on building great applications. Explore our simple and scalable video API at https://liveapi.com.