Ever wonder how a YouTube video shows up perfectly inside a blog post, or a Google Map appears on a company’s contact page? The magic behind that is something called an embed code.
It’s essentially a small piece of code you copy from one website and paste onto your own. Think of it as a digital frame; you’re not actually putting the painting (the content) on your wall, but hanging a frame that shows a live view of it from the original gallery.
Unlocking Dynamic Content with Embed Codes

Let’s stick with that painting analogy. Instead of trying to describe a masterpiece to a friend, you could just hang it on your wall for them to see. That’s exactly what an embed code does for your website. You’re not making a copy of the content; you’re creating a window that displays it directly from its source.
This simple copy-and-paste action is a game-changer for anyone managing a website. It lets you add all sorts of engaging, interactive elements to your pages without knowing a lick of programming.
Why It’s So Common
Embedding has become a cornerstone of modern web design because it’s incredibly effective and easy. It allows anyone, regardless of technical skill, to integrate rich media and make their site more interesting.
Just look at the numbers. Platforms like WordPress, which powers over 43% of all websites, have built-in features and plugins dedicated to embedding. This widespread adoption proves just how vital embedding is for creating the dynamic web experiences we all expect today. For a great example, check out how our partners at Timepath explain embedding timelines.
The core idea is simple: You don’t host it, you just show it. This keeps your website fast and ensures the content you display is always up-to-date, as any changes made at the source are automatically reflected on your page.
How an Embed Code Actually Works
So, what’s really happening when you drop an embed code onto your page? Think of your website as an art gallery. You could hang a copy of a famous painting, but an embed code does something much cooler. It’s like cutting a window in your gallery wall that looks directly into another museum, showing the original artwork in real-time.
That “window” is technically an <iframe>, which stands for inline frame. It’s a simple piece of HTML that tells a web browser to load a separate webpage right inside the current one.
This screenshot from Wikipedia shows a classic <iframe> element. The most critical part is the src attribute—that’s the source URL pointing to the content you want to display inside the frame.
The Source Server Advantage
One of the biggest wins here is that the embedded content—your video, podcast, or map—doesn’t actually live on your website. When you embed a YouTube video, it’s still hosted and streamed from YouTube’s powerful servers, not yours.
This is a massive benefit. You get to feature engaging, media-rich content without it eating up your own server’s storage or bandwidth. Your website stays lean and loads quickly because all the heavy lifting is handled by a platform designed specifically for that job. This principle of serving media efficiently from a dedicated source is also the backbone of modern streaming tech, like the protocols behind HTTP live streaming.
The core principle is efficiency. The embed code is just a lightweight pointer, telling the browser, “Go get the content from over there and show it right here.”
Keeping Content Current Automatically
Another fantastic perk is that this connection to the original source is live and dynamic. If the creator of that YouTube video updates the title or swaps out the thumbnail, those changes instantly reflect on your website. No action is needed on your part.
This live link means your embedded content never gets stale or outdated. You don’t have to manually check for updates or re-upload anything; the iframe takes care of it all. It’s a powerful, time-saving strategy that ensures your audience always sees the latest version of the content.
Why Using Embed Codes Is a Smart Move

So, you know what an embed code is and how it works. But the real question is, why should you bother using them in the first place? It turns out, embedding content is one of the smartest things you can do for your website. It’s a strategic play that pays off in everything from user engagement to your site’s overall authority.
Think about it: when you add things like videos, audio players, or social media feeds, you’re giving people more to do than just read. They can watch, listen, and interact. This transforms a static page into a dynamic, memorable experience, giving visitors a compelling reason to stick around.
Boost User Engagement and SEO
That extra interaction isn’t just a nice-to-have; it delivers real, measurable benefits. When a page has dynamic, embedded elements, it grabs and holds a visitor’s attention. In fact, some studies have shown an increase in average session duration of up to 40% compared to pages with only static text. You can read more about these content engagement findings from Adobe Analytics on timepath.co.
This increase in “dwell time” is a massive signal to search engines. When Google sees people spending more time on your site, it assumes your content is high-quality and relevant, which can give your rankings a healthy boost.
By featuring authoritative content from other platforms, you essentially borrow their credibility. You’re showing both users and search engines that your site is a well-researched hub of useful information.
There’s another huge win here: embedding saves you the technical nightmare of hosting large media files yourself. Videos are the perfect example. They eat up bandwidth and demand a sophisticated setup to stream without constant buffering. For anyone serious about video, figuring out the best CDN for video streaming is non-negotiable for a good user experience. An embed code simply hands all that heavy lifting over to platforms that were built for it.
Real-World Examples of Embedded Content
Chances are you’ve already seen embedded content dozens of times today without even realizing it. The embed code is the secret sauce that makes the modern web feel so connected and alive. Once you know what to look for, you’ll start seeing it everywhere.
Think about a news article you recently read about a big event. Instead of just describing a speech, the journalist probably dropped the full video right into the page, straight from YouTube. That little video player is an embed, and it lets you see the source for yourself, adding a layer of trust and engagement that plain text just can’t deliver.
Or how about an artist promoting their new album on their blog? They can embed a player directly from a platform like SoundCloud or Spotify. This is a game-changer because fans can listen right then and there, turning a simple announcement into an instant listening party.
What Can You Actually Embed?
The beauty of embedding lies in its incredible versatility. It’s not just for videos or music; it solves all sorts of practical problems for websites, big and small. From interactive maps to social media feeds, embedding brings external content seamlessly into your own digital space.
To give you a better idea of the possibilities, here’s a quick look at some common types of embedded content.
Types of Content You Can Embed
| Content Type | Common Source | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Videos | YouTube, Vimeo | Showcasing product demos, tutorials, or event highlights. |
| Audio | Spotify, SoundCloud | Sharing podcasts, music tracks, or interview clips. |
| Social Posts | X (Twitter), Instagram | Displaying real-time customer testimonials or company news. |
| Maps | Google Maps | Providing interactive directions to a physical location. |
| Forms/Surveys | Google Forms, SurveyMonkey | Gathering customer feedback or registrations within a post. |
| Presentations | SlideShare, Google Slides | Sharing conference slides or business presentations. |
As you can see, the list goes far beyond just media. You can embed just about any piece of content that has its own home on another service.
Here are a few more popular examples in action:
- Live Social Media Feeds: A brand can pull its live Twitter (X) or Instagram feed directly onto its website homepage. This is a great way to show off fresh updates and real-time customer conversations.
- Interactive Maps: A restaurant’s contact page is a thousand times more useful when it includes an embedded Google Map. Customers don’t have to leave the site; they can get directions with a single click.
- Surveys and Forms: A marketer can drop a Google Form or SurveyMonkey poll right into a blog post to gather feedback, completely removing the hassle of sending people to another website.
The real goal of embedding is simple: bring the power and functionality of another platform directly to your audience, right where they already are. It closes the gap between your content and the interactive tools that make it better.
This is especially crucial on platforms that don’t let you upload certain files directly. For example, you can’t just upload an MP4 video file to a Shopify blog post. Instead, you must upload it to a service like YouTube or Vimeo first and then paste the embed code. This simple step ensures the video plays smoothly for every single visitor.
Ultimately, once you understand what an embed code is and how to use it, you unlock a ton of new ways to make your website more dynamic, engaging, and genuinely useful for your audience.
How to Embed Content on Your Website
So, you’re ready to start embedding content on your own site? You’ll be happy to know it’s a lot easier than it sounds. The process is pretty much the same no matter what platform you’re grabbing the content from.
Let’s use the most common scenario as our guide: embedding a YouTube video.
First thing’s first: you have to find that little snippet of code. On YouTube, just look for the Share button right below the video. When you click it, a few options will pop up—you want to hit “Embed”. A new window will appear showing you a block of HTML code, which usually kicks off with <iframe>.
That’s it. That’s your embed code. Almost every platform gives you a handy “Copy” button to grab the whole thing in one click, which helps avoid any copy-paste mistakes.
Placing the Code on Your Site
Once you’ve got the code copied, you just need to paste it into your website’s backend. How you do this really depends on what you use to manage your site, whether it’s a CMS like WordPress or you’re coding directly in HTML.
- For WordPress: In the page or post editor, look for the “Custom HTML” block. Just add that block and paste your code right into it.
- For other CMS platforms: You’re looking for something similar. It might be called an “HTML,” “Code,” or “Embed” widget. The idea is always the same: you need a special place to drop in raw code.
- For plain HTML: Simply paste the
<iframe>snippet right into the<body>of your HTML file, exactly where you want the video to show up.
This simple visual breaks down the three main steps.
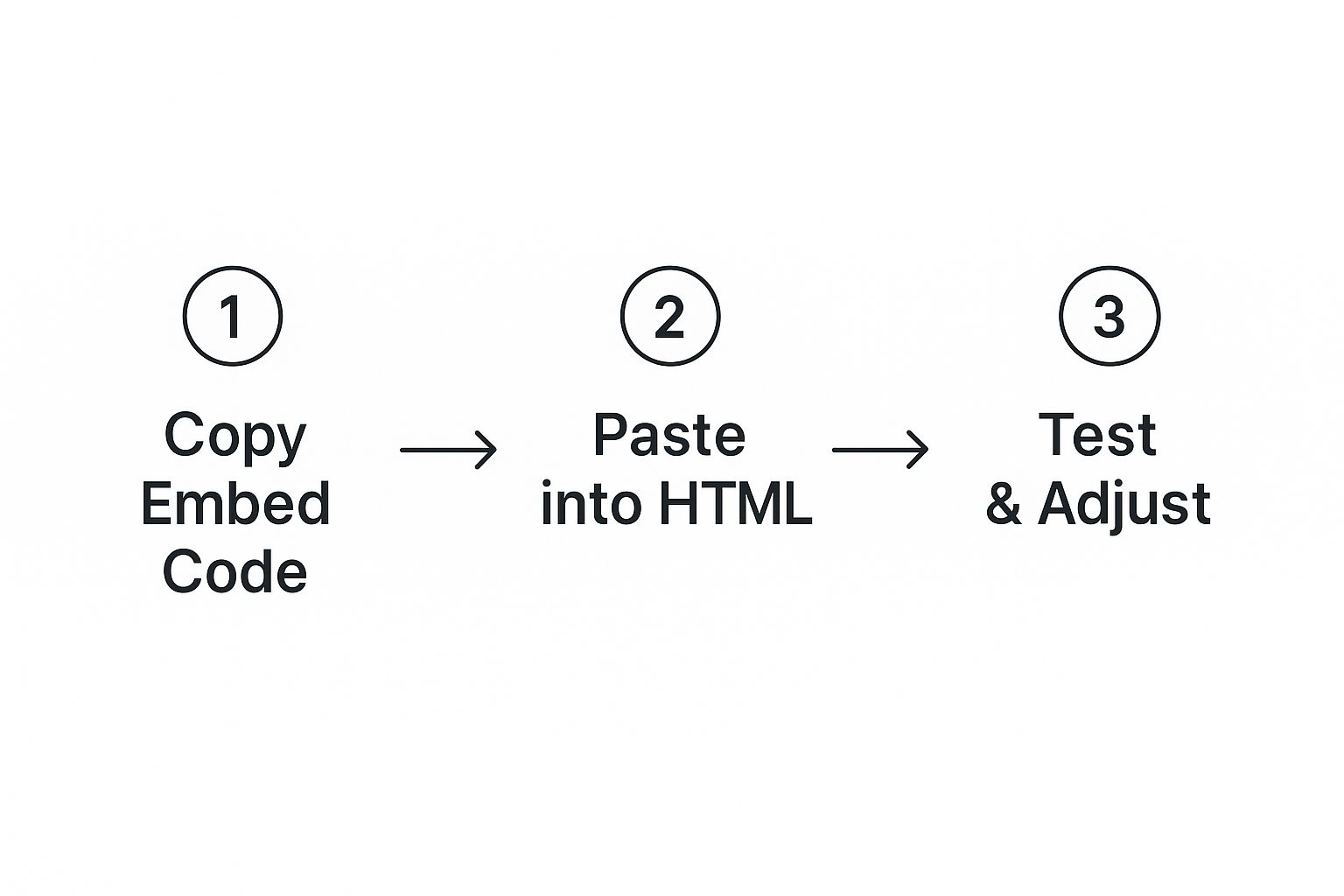
It really is just a simple flow: find the code, copy it, and paste it where it needs to go. This same basic process works for almost any type of embeddable media from any source.
Pro Tip: Always preview your page after you paste the code. This quick check makes sure everything loaded properly and looks right with the rest of your content. If the video looks too big or too small, you can usually tweak the width and height numbers right inside the embed code itself.
The same logic applies when you want to add other media, like live video. For a more detailed walkthrough on that, check out our guide on how to embed a live stream on your website.
Playing it Safe: How to Embed Content the Smart Way
Using an embed code is pretty straightforward, but a little bit of know-how can go a long way in protecting your website and keeping your visitors happy. Think of these as the rules of the road for embedding—they’ll help you steer clear of common problems.
Stick to Sources You Trust
This is the big one. You should only ever embed content from sources you know and trust. Why? Because a bad actor could slip malicious code into an embed, potentially opening up your site to security risks or even tracking your visitors without you knowing.
When in doubt, stick with the household names you already know, like YouTube, Vimeo, and Google Maps.
Keep Your Site Fast and Mobile-Friendly
It’s tempting to load up a page with cool embedded content, but be careful. Each embed adds another task for the browser, and too many can bog down your site, leading to slow load times. My advice? Be picky. Only embed content that genuinely adds value to the page.
For heavier content like videos, look into a technique called lazy loading. It’s a clever trick that waits to load the video until a visitor actually scrolls down to it. This can make a huge difference in how fast your page initially loads.
One last thing: always, always check how your embedded content looks on a phone. That beautiful video player on your desktop could be a disaster on a smaller screen, completely breaking your page layout. Make sure your embeds are responsive, meaning they’ll automatically resize to look great on any device.
Got Questions About Embed Codes? We’ve Got Answers.
As you start working with embed codes, you’ll probably run into a few head-scratchers. It’s completely normal. Let’s tackle some of the most common questions that pop up so you can move forward with confidence.
Is It Legal to Use an Embed Code? Am I Violating Copyright?
This is a big one, but the answer is usually straightforward: no, it’s not a copyright violation.
When a platform like YouTube or Vimeo gives you an “Embed” button, they are explicitly granting you permission to display that content on your site. Think of it as an official license. You’re just creating a window to their content, not stealing it.
What would be a copyright violation is downloading their video and re-uploading it to your own server. Always stick to the official embed feature, and you’ll stay on the right side of the law.
The key is using the approved method. The platform grants permission through the embed functionality itself, creating a legitimate way to share content without infringing on copyright.
Can I Just Embed Any Website I Want on My Page?
Nope, you can’t. Many websites have security measures in place to prevent their pages from being displayed inside an <iframe> on another domain.
This isn’t them being difficult; it’s a crucial security practice to prevent something called “clickjacking,” where attackers trick users into clicking on something they didn’t intend to. So, you can only embed content from sources that have specifically decided to allow it.
Will Embed Codes Make My Website Slower?
They certainly can. Every piece of embedded content—a video player, a social media feed, an interactive map—adds another task for the browser. It has to make a separate request to an external server to fetch that content, which can add to your page’s load time.
A couple of embeds here and there are perfectly fine. But if you pack a single page with a dozen high-resolution videos, you’re almost guaranteed to see a noticeable slowdown. It’s all about balance.
Ready to add professional, high-quality live video to your own application? With LiveAPI, you get a powerful, developer-friendly platform for all your streaming and on-demand video needs. Start building with LiveAPI today.










