At its core, a video codec is the technology that makes digital video practical. It’s a piece of software or hardware that compresses and decompresses video files so they’re small enough to be stored or streamed across the internet.
Think of it like a specialized tool for packing a suitcase. The codec takes a massive, unpacked suitcase of raw video data and cleverly folds and squeezes it down for travel (this is encoding). When it reaches its destination, it unpacks everything perfectly so you can see it on your screen (this is decoding). This compression-decompression cycle is the unsung hero behind every YouTube video, Netflix binge, and video call you make.
Why Do We Even Need Codecs?
Ever wondered how a massive, crystal-clear 4K movie file can stream to your phone without eating up your entire data plan in minutes? The answer is codecs. Without them, the video-rich internet we take for granted simply couldn’t exist.
Raw, uncompressed video files are gigantic. Just one minute of 1080p HD video can easily top a gigabyte of data. Trying to send that much information in real-time would bring most internet connections to a grinding halt.
This is where a codec saves the day. It systematically analyzes the video and throws out redundant information that the human eye won’t notice, making the file drastically smaller.
To help you get a grip on the key terms, here’s a quick breakdown of the core concepts.
Codec Key Concepts at a Glance
This table breaks down the core functions and terms related to video codecs for quick reference.
| Term | Simple Analogy | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| Codec | A language translator | A program that compresses (encodes) and decompresses (decodes) video data. |
| Encoding | Packing a suitcase | The process of shrinking a large, raw video file into a smaller, manageable size. |
| Decoding | Unpacking a suitcase | The reverse process of reconstructing the compressed file into a viewable video on a device. |
| Compression | Creating a summary | The art of reducing file size by removing redundant or less noticeable data. |
These simple processes are what make modern video streaming possible.
The Evolution of Making Video Smaller

The history of codecs is really a story of a relentless push for better efficiency. While early MPEG standards in the 1990s laid the groundwork, the release of H.264 (AVC) in 2003 was a massive leap forward.
Suddenly, we had a codec that offered roughly 50% better compression than anything that came before it at the same level of quality. This breakthrough wasn’t just a technical improvement; it was the engine that powered the explosion of online streaming services like YouTube and the adoption of high-definition Blu-ray discs.
You can learn more about the evolution of advanced video coding to see just how foundational these standards were. This constant innovation is what allows us to stream higher-quality video on slower connections today.
How Video Codecs Shrink Your Video Files

So, what’s really happening under the hood when a codec gets to work? It’s all about being smart with the data. Codecs use clever compression algorithms to shrink video files—often by 90% or more—without you ever noticing a dip in quality.
Think of it like making a flipbook animation of someone waving hello. You wouldn’t redraw the entire background and the person on every single page, right? You’d just redraw the part that’s moving: their arm. This is the exact same logic behind a powerful technique called inter-frame compression.
Predicting What Comes Next
At its core, a video is just a rapid-fire sequence of still images, which we call frames. In almost any video, not much actually changes from one frame to the next.
Inter-frame compression takes full advantage of this. It establishes certain frames as “key frames,” which are complete, high-quality images. For all the frames in between, the codec doesn’t bother saving the whole picture again. Instead, it just records what changed—the tiny “deltas” from the frame before it.
This is a lifesaver for scenes with very little movement, like a person talking at a desk. For a high-action car chase, it needs a bit more data to keep up, but the principle is the same.
Key Takeaway: By only storing the changes between frames instead of the entire picture every time, inter-frame compression slashes the amount of data needed to represent the video.
Finding Efficiencies in a Single Frame
Even within a single, static picture, there are ways to save space. That’s where intra-frame compression enters the picture. Think of it as creating a shorthand for describing an image.
If a huge patch of the frame is just blue sky, the codec doesn’t need to store the color information for every single one of those pixels. It can just say, “this whole block is blue.” It finds these repetitive patterns and textures within the frame and simplifies them.
These two strategies, working in tandem, are constantly performing a delicate balancing act between three crucial elements:
- File Size: How compact the final video file becomes.
- Visual Quality: How good the compressed video looks compared to the original.
- Computational Power: How much processing muscle it takes to encode and decode the video.
A Field Guide to the Most Common Video Codecs
Now that we’ve demystified how video compression works, let’s meet the main players in the video codec world. Think of this as getting to know the technologies you interact with every single day, whether you’re scrolling through a social feed or settling in for a movie night. Each one has its own personality, with distinct strengths, weaknesses, and ideal scenarios.
The image below gives a great visual breakdown of the two main compression philosophies, showing the constant balancing act between shrinking file sizes and keeping the picture sharp.
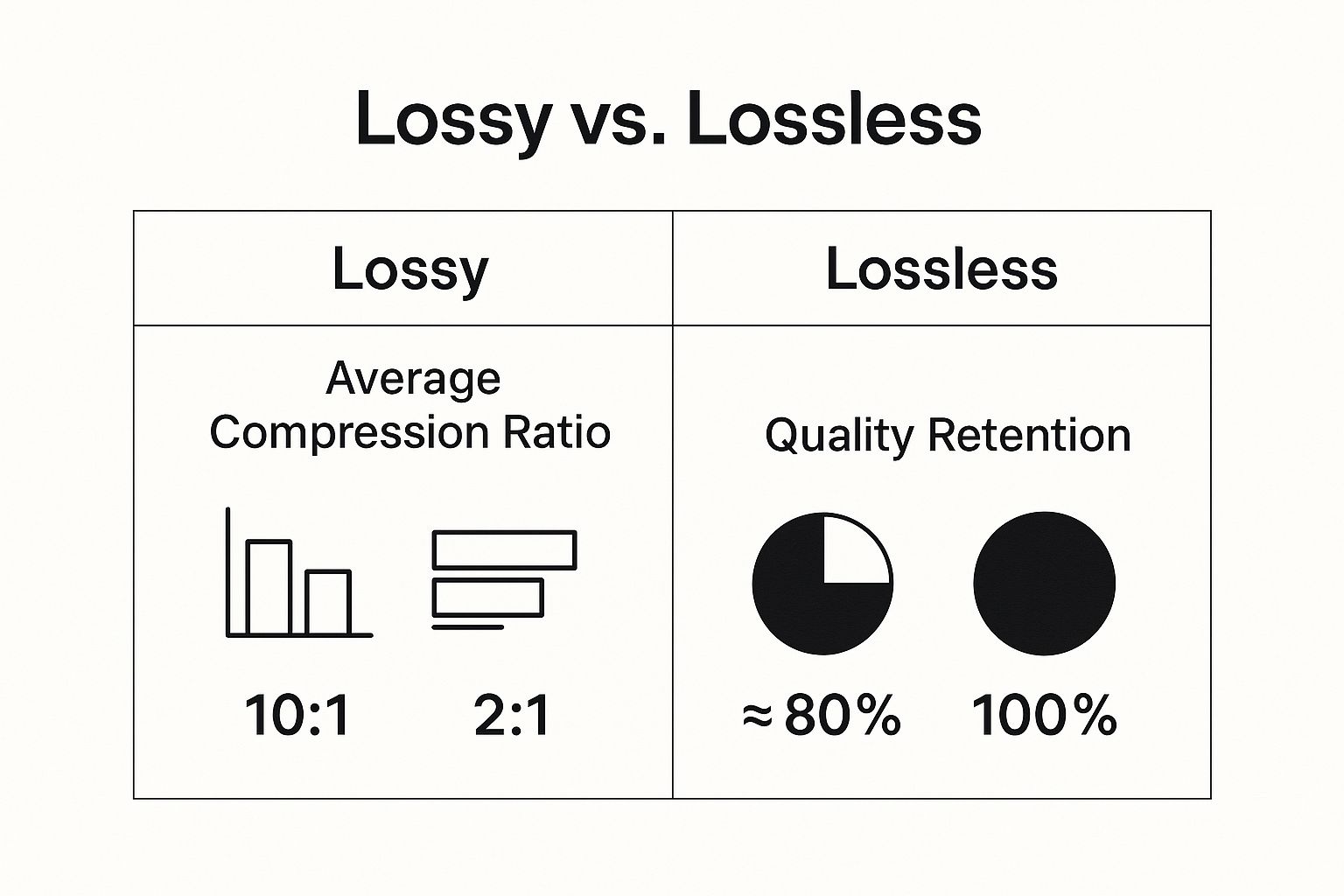
As you can see, lossy compression makes files dramatically smaller by strategically dropping some visual data, whereas lossless keeps every single pixel intact but doesn’t shrink the file nearly as much.
H.264: The Universal Standard
First on our list is H.264, also known by its technical name, Advanced Video Coding (AVC). If one codec truly defined the modern age of streaming, this is it. Rolled out way back in 2003, its combination of solid compression and broad device support is what allowed services like YouTube and Netflix to become household names.
H.264 hits a sweet spot between video quality and the processing power needed to play it back. That’s why it’s still the most compatible and widely used codec on the planet, making sure your video works flawlessly on everything from a brand-new smart TV to a smartphone from a few years ago. It’s the dependable engine for HD streaming.
H.265: The 4K Successor
As our screens got bigger and resolutions leaped into the 4K era, the world needed a smarter way to compress video. That’s where H.265, or High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), comes in. The name says it all—it was built from the ground up to be a more efficient successor to H.264.
HEVC can deliver the same visual quality as H.264 while using up to 50% less data. This makes it the go-to choice for streaming ultra-high-definition 4K and HDR content without needing a massive internet connection.
But there’s a catch. Its adoption has been slower than expected, mostly due to complicated and often expensive patent licensing. While it’s the standard for things like 4K Blu-rays and premium streaming tiers, its journey to becoming a universal standard has been bumpy.
VP9 and AV1: The Royalty-Free Powerhouses
The licensing headaches around HEVC created an opening for a new approach: open-source, royalty-free alternatives. Google stepped up with VP9, the codec that now powers a huge chunk of YouTube’s high-resolution video. It delivers compression that’s on par with H.265 and works great across most modern web browsers and Android devices.
Taking that idea a step further, a powerhouse group of tech companies—including Google, Amazon, and Netflix—collaborated to create AV1. This is the next generation. AV1 is even more efficient, promising another 30% reduction in file size compared to both HEVC and VP9. It does demand more processing power to encode, but for delivering the absolute best quality with the least amount of data, AV1 is clearly the future.
Comparing Popular Video Codecs H.264 vs H.265 vs VP9 vs AV1
To make sense of these options, it helps to see them side-by-side. This table breaks down their key differences in efficiency, compatibility, and what they’re best used for.
| Codec | Compression Efficiency | Compatibility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| H.264 (AVC) | Good | Universal (99%+ of devices) | Live streaming, VOD, social media, web video |
| H.265 (HEVC) | Excellent (up to 50% better than H.264) | Widespread but licensing can be an issue | 4K/8K UHD streaming, premium content, Blu-ray |
| VP9 | Excellent (similar to H.265) | Most modern browsers, Android | YouTube, high-quality web streaming |
| AV1 | Exceptional (up to 30% better than H.265/VP9) | Growing (supported by major browsers & platforms) | Next-gen streaming, saving bandwidth, future-proofing |
Choosing the right codec is always a trade-off. While H.264 offers unmatched compatibility, newer codecs like AV1 provide incredible efficiency for delivering high-quality streams to modern devices.
Why Next-Generation Codecs Like AV1 Are a Game Changer

The push for better and better video quality never stops. As we’ve moved from standard HD to incredible 4K, 8K, and even fully immersive VR, the raw video files have become absolutely massive. Trying to send that much raw data over a typical internet connection is like trying to force a river through a garden hose. It just doesn’t work.
This is exactly where next-generation codecs like AV1 come into the picture. They aren’t just minor tweaks on old technology; they’re built from the ground up to be incredibly efficient at compression. Their whole purpose is to wrestle these gigantic files into a manageable size for streaming, all without losing the crisp detail that makes high-resolution video so amazing.
Fueling the Future of Media
It’s no surprise that the demand for these sophisticated compression tools is exploding. This trend is directly linked to our collective hunger for higher-quality video and new formats like virtual reality.
The market for next-gen video codecs is expected to jump from roughly USD 4.27 billion in 2024 to an incredible USD 25.77 billion by 2033. That staggering growth tells you everything you need to know about how vital this technology is for the future of all digital media.
This massive acceleration was kicked into high gear by the global shift to remote work and streaming everything for entertainment, putting a huge strain on our internet infrastructure. If you’re curious, you can dig deeper into this booming market for next-generation video codecs.
Codecs like AV1 are essential for building a more sustainable digital world. They are the key to unlocking several major advancements:
- Buffer-Free 8K Streaming: Imagine watching cinema-quality video on your smart TV without a single frustrating loading wheel.
- Immersive Virtual Worlds: Powering complex VR and AR experiences that depend on huge amounts of data being delivered with almost zero lag.
- Reduced Internet Congestion: By making video files smaller, these codecs lighten the load on global networks, helping create a faster, more reliable internet for everyone.
By making these kinds of experiences possible, modern codecs are truly paving the way for the next chapter in how we consume entertainment and interact online.
How LiveAPI Manages Codecs for Flawless Streaming
It’s one thing to know the difference between H.264, VP9, and AV1. It’s another thing entirely to try and manage all those codecs for a global audience. That’s where a platform like LiveAPI comes in to do the heavy lifting for you.
You don’t need to be a video compression expert to deliver a perfect, buffer-free experience to every viewer. You just send us a single, high-quality video stream, and our system immediately gets to work.
We use a process called transcoding. Think of it like a video “master key” system. We take your original stream and instantly re-encode it into a whole range of different formats, resolutions, and quality levels. This creates a complete set of streams, ready for any situation—from a high-bitrate AV1 stream for the latest devices to a universally compatible H.264 stream for older hardware.
Powering Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Having all these different versions of your stream is what makes adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) possible. Instead of trying to force one giant video file on every viewer, ABR is smart enough to deliver the right version to each person in real-time.
LiveAPI automatically figures out what kind of device each viewer is using and how fast their internet connection is. It then picks the best possible stream from the transcoded options to guarantee a smooth playback experience.
So, what does this look like in the real world?
- A viewer on a new laptop with a fast fiber connection? They’ll get a beautiful, crystal-clear 4K stream using the super-efficient AV1 codec.
- Someone watching on an older phone with a spotty 4G connection? They’ll receive a lower-resolution H.264 stream that plays perfectly without constant buffering.
This isn’t a one-time decision, either. The system constantly monitors the connection. If a viewer’s Wi-Fi suddenly gets flaky, the player will instantly switch to a lower-quality stream to keep the video from stopping.
The end result? A flawless, high-quality stream for every single user, no matter what device they’re on or where they are in the world.
How to Choose the Right Codec for Your Project
Alright, we’ve covered what codecs are and looked at the big players. So, how do you actually choose one? It’s not as simple as just picking the newest, shiniest option. The best codec for you is the one that fits your project’s specific needs, your audience, and your budget.
Making the right call here means your video will look great and play smoothly for everyone you’re trying to reach. To get there, you just need to answer a few key questions about your goals.
The Three Big Questions to Ask
Think of this as a balancing act between three critical factors. Your answers will naturally point you toward the best codec for the job.
- Who is your audience? If you need to reach the widest possible audience on all sorts of devices—including older phones and computers—then H.264 is your safest bet. Its universal support is still unmatched.
- What quality are you aiming for? If your goal is to deliver breathtaking 4K or 8K video without demanding a massive internet connection from your viewers, then a modern codec like AV1 is the way to go. It’s built for high-resolution, low-bandwidth streaming.
- What’s your budget for licensing? Worried about royalty fees? Open-source, royalty-free codecs like VP9 and AV1 are your friends. They help you avoid the potentially expensive and complicated licensing that comes with H.265 (HEVC).
By thinking through the trade-offs between reach, quality, and cost, you’re turning a technical decision into a strategic one. It’s about aligning the technology with what you’re ultimately trying to achieve.
This kind of strategic thinking is more important than ever. The demand for better video compression is exploding, especially in North America, which accounts for over 36% of the market. With 4K/8K content and 5G networks becoming the norm, the industry needs codecs that can deliver flawless quality without compromise. You can dive deeper into the numbers and see how the global video decoder market is projected to grow.
Choosing a codec is a crucial step, but it’s just one part of the streaming puzzle. LiveAPI is designed to handle this for you, automatically transcoding your video to ensure every single viewer gets the best possible experience, no matter their device or connection. Get started with LiveAPI and take the complexity out of streaming.